Unveiling the Hidden World: Lifecycles of Pathogenic Protists in Humans

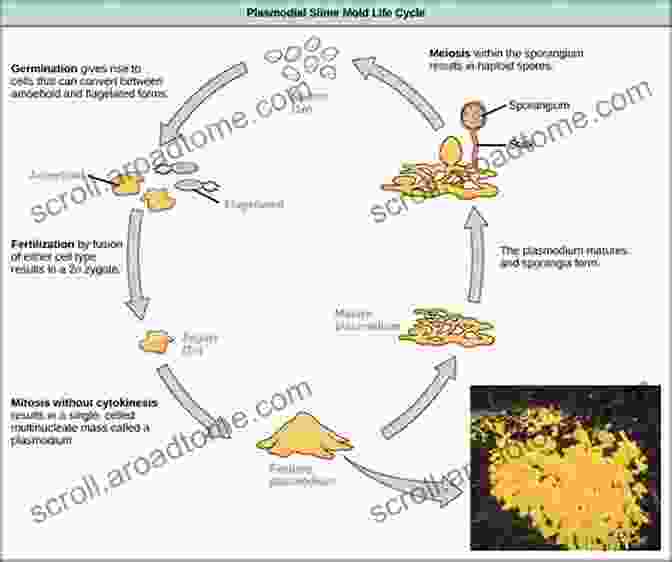
Pathogenic protists are microorganisms that cause diseases in humans. They are eukaryotic organisms, meaning they have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Protists are found in a variety of habitats, including water, soil, and even the human body.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 103794 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 1156 pages |
Some of the most common protists that cause disease in humans include:
* Giardia lamblia, which causes giardiasis, a diarrheal disease * Cryptosporidium parvum, which causes cryptosporidiosis, another diarrheal disease * Toxoplasma gondii, which causes toxoplasmosis, a disease that can be particularly dangerous for pregnant women and people with weakened immune systems * Plasmodium falciparum, which causes malaria, a deadly disease that is transmitted by mosquitoes
Lifecycles of Pathogenic Protists
The lifecycles of pathogenic protists vary depending on the species. However, there are some general stages that are common to most protists.
1. Infection: The lifecycle begins when a protist infects a human host. This can happen in a variety of ways, such as through ingestion of contaminated food or water, or through contact with an infected animal. 2. Trophic stage: Once inside the host, the protist enters a trophic stage, during which it feeds and grows. This stage can be asexual or sexual, depending on the species of protist. 3. Transmission stage: After the trophic stage, the protist enters a transmission stage, during which it is passed from one host to another. This can happen through a variety of mechanisms, such as through contact with infected feces or urine, or through the bite of an infected insect.
Pathogenesis of Protists
The pathogenesis of protists is complex and varies depending on the species of protist. However, there are some general mechanisms by which protists can cause disease in humans.
* Direct damage: Some protists can directly damage host cells by releasing toxins or by invading and destroying cells. * Immune response: The human immune system can react to protists by producing antibodies and other immune cells. This can lead to inflammation and tissue damage. * Opportunistic infections: Some protists can take advantage of weakened immune systems to cause disease. This is often the case in people with HIV/AIDS or other chronic diseases.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Protists
The diagnosis of protists is typically made based on symptoms and a physical examination. However, laboratory tests may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
The treatment of protists depends on the species of protist. Some protists can be treated with antibiotics, while others require more specific treatment.
Prevention of Protists
There are a number of things that can be done to prevent infection with protists. These include:
* Washing hands: Washing hands with soap and water is one of the most effective ways to prevent infection with protists. * Drinking clean water: Drinking only clean water can help to prevent infection with protists that are transmitted through water. * Eating safe food: Cooking food thoroughly can help to kill protists that may be present in the food. * Avoiding contact with infected animals: Avoiding contact with infected animals can help to prevent infection with protists that are transmitted through animals.
Pathogenic protists are a major cause of disease in humans. Understanding the lifecycles of these protists is essential for developing effective strategies for prevention and treatment.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 103794 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 1156 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Bud Beamer
Bud Beamer Kim Michele Richardson
Kim Michele Richardson Carol Burnett
Carol Burnett Richard Furman
Richard Furman Brooks D Kubik
Brooks D Kubik Cas Holmes
Cas Holmes Caroline Foster
Caroline Foster Brooks Agnew
Brooks Agnew C P Aiden
C P Aiden John R Monteith
John R Monteith Stephanie L Tourles
Stephanie L Tourles Chris Collingwood
Chris Collingwood Campbell Devine
Campbell Devine Bryan Collier
Bryan Collier Cameron Soran
Cameron Soran Nicolette Andrews
Nicolette Andrews Tom Lansford
Tom Lansford Don Failla
Don Failla Tanis Helliwell
Tanis Helliwell Carol Graham
Carol Graham
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Joel MitchellUnveiling Nature's Fury: Earthquakes – Risk Detection, Warning, and Research
Joel MitchellUnveiling Nature's Fury: Earthquakes – Risk Detection, Warning, and Research
 John SteinbeckOracle Belline Complete Training: A Journey Through the Realm of Intuition...
John SteinbeckOracle Belline Complete Training: A Journey Through the Realm of Intuition...
 Deacon BellSlice of Britain by Caroline Taggart: A Journey Through the Cultural Delights...
Deacon BellSlice of Britain by Caroline Taggart: A Journey Through the Cultural Delights... Gene SimmonsFollow ·19.5k
Gene SimmonsFollow ·19.5k Edwin BlairFollow ·7.7k
Edwin BlairFollow ·7.7k Stuart BlairFollow ·10.2k
Stuart BlairFollow ·10.2k Jace MitchellFollow ·6.4k
Jace MitchellFollow ·6.4k Davion PowellFollow ·16.5k
Davion PowellFollow ·16.5k Greg CoxFollow ·13.6k
Greg CoxFollow ·13.6k Edwin CoxFollow ·18.4k
Edwin CoxFollow ·18.4k Preston SimmonsFollow ·17.7k
Preston SimmonsFollow ·17.7k

 Shawn Reed
Shawn ReedEmbark on a Transformative Journey: Discover Ritual...
Delve into the Enigmatic World of...

 Connor Mitchell
Connor MitchellUnleash Your Soul: A Journey to Less Noise, More Soul
Embrace the Power of Silence...

 Derek Cook
Derek CookRitual Theory, Ritual Practice: Unlocking the Secrets of...
Rituals have been an...

 Evan Hayes
Evan HayesStop the Itch: Simple Steps to Lasting Relief
Itching, an...

 Herman Mitchell
Herman MitchellThe Ultimate Premarital Guide: Your Essential Wedding...
Congratulations on your engagement! This is...

 DeShawn Powell
DeShawn PowellUnlocking the Enigma of the Mantle: A Deep Dive into "The...
Our planet,...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 103794 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 1156 pages |