Distribution and Determinants of Disease: A Comprehensive Guide to Public Health Basics

Understanding the distribution and determinants of disease is a critical cornerstone of public health. It provides invaluable insights into the underlying factors that influence disease patterns and helps shape effective interventions to prevent and control health threats. This article will delve into the intricate world of disease distribution and determinants, examining the key concepts, methodologies, and implications for public health practice.
Distribution of Disease
The distribution of disease refers to the patterns in which diseases occur across populations and geographic regions. These patterns can vary significantly, ranging from highly localized outbreaks to widespread pandemics. Understanding the distribution of disease is essential for identifying high-risk areas, targeting interventions, and monitoring the progress of disease control efforts.
4.4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 44788 KB |
| X-Ray for textbooks | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 276 pages |
Epidemiological Measures of Disease Distribution
Epidemiologists use various measures to describe the distribution of disease, including:
- Incidence: The number of new cases of a disease that occur within a specific population during a defined period.
- Prevalence: The total number of cases of a disease that exist within a population at a specific point in time.
- Mortality: The number of deaths caused by a specific disease within a population during a defined period.
Factors Influencing Disease Distribution
The distribution of disease is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Environmental factors: Climatic conditions, air and water quality, and access to sanitation can significantly impact disease transmission.
- Socioeconomic factors: Income, education, housing conditions, and access to healthcare affect disease susceptibility and outcomes.
- Behavioral factors: Smoking, alcohol consumption, unhealthy diet, and lack of physical activity can increase the risk of certain diseases.
- Genetic factors: Some diseases have a genetic predisposition, particularly when combined with other environmental and behavioral influences.
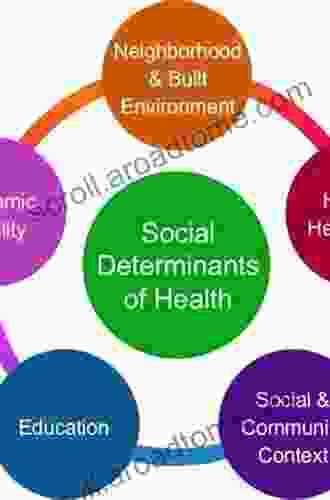
Determinants of Disease
Determinants of disease are the underlying factors that contribute to the occurrence and progression of diseases. These determinants are often categorized into two broad groups:
Biological Determinants
Biological determinants encompass inherited characteristics and physiological factors that influence an individual's susceptibility to disease. These include:
- Age: Certain diseases are more common in specific age groups due to physiological changes and immune system development.
- Genetics: Genetic traits can predispose individuals to certain diseases or increase their severity.
- Immunological status: A weakened immune system can make individuals more susceptible to infections and other diseases.
Social Determinants
Social determinants encompass societal factors that influence health outcomes and disease patterns. These include:
- Income and poverty: Low income and socioeconomic status are associated with increased risk of disease and poor health outcomes.
- Education: Education level influences health literacy, access to healthcare, and health-promoting behaviors.
- Housing: Overcrowding, lack of sanitation, and poor housing conditions can contribute to disease transmission and poor health.
- Social support: Strong social support networks can promote health and well-being, while isolation and loneliness can increase disease risk.
- Access to healthcare: Availability, affordability, and quality of healthcare services significantly impact disease prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
Implications for Public Health Practice
Understanding the distribution and determinants of disease has profound implications for public health practice:
- Targeted Interventions: Identifying high-risk populations and geographic areas allows public health officials to tailor interventions to specific needs and vulnerabilities.
- Prevention and Control: By addressing underlying determinants, public health measures aim to prevent diseases from occurring or spreading.
- Health Promotion: Public health campaigns focus on promoting healthy behaviors and reducing risk factors to improve overall health and prevent disease.
- Surveillance and Monitoring: Tracking disease patterns and monitoring determinant changes are essential for early detection of outbreaks and timely response.
- Health Policy Development: Evidence from disease distribution and determinant studies informs policy decisions aimed at improving population health and reducing health disparities.
Understanding the distribution and determinants of disease is a fundamental pillar of public health. By analyzing disease patterns and identifying underlying factors, public health professionals can develop effective interventions to prevent and control health threats, promote health and well-being, and create healthier communities for all.
4.4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 44788 KB |
| X-Ray for textbooks | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 276 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Maurice Isserman
Maurice Isserman Carol K Mack
Carol K Mack Kurtis Foote
Kurtis Foote Cheryl Eichar Jett
Cheryl Eichar Jett Carli Mcconkey
Carli Mcconkey Carolyn Steele Agosta
Carolyn Steele Agosta Mark Louis Rybczyk
Mark Louis Rybczyk Michael B Junge
Michael B Junge Camilla Kristiansen
Camilla Kristiansen Hilary M Lips
Hilary M Lips Yvonne Caputo
Yvonne Caputo Camille Seaman
Camille Seaman Kimberly Gatto
Kimberly Gatto Terrell L Hill
Terrell L Hill Deb Gleason
Deb Gleason Ian Christe
Ian Christe Carol Fung
Carol Fung John Smiley
John Smiley Mark Mittelberg
Mark Mittelberg Charlot King
Charlot King
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Ron BlairLights, Camera, Braces: Dr. Samantha Wrighting, the Trailblazing Orthodontist...
Ron BlairLights, Camera, Braces: Dr. Samantha Wrighting, the Trailblazing Orthodontist... Bradley DixonFollow ·11k
Bradley DixonFollow ·11k Isaac AsimovFollow ·11k
Isaac AsimovFollow ·11k George R.R. MartinFollow ·11.6k
George R.R. MartinFollow ·11.6k Barry BryantFollow ·9.7k
Barry BryantFollow ·9.7k Sam CarterFollow ·16k
Sam CarterFollow ·16k James GrayFollow ·10.1k
James GrayFollow ·10.1k Ashton ReedFollow ·5.6k
Ashton ReedFollow ·5.6k Pete BlairFollow ·9.4k
Pete BlairFollow ·9.4k

 Shawn Reed
Shawn ReedEmbark on a Transformative Journey: Discover Ritual...
Delve into the Enigmatic World of...

 Connor Mitchell
Connor MitchellUnleash Your Soul: A Journey to Less Noise, More Soul
Embrace the Power of Silence...

 Derek Cook
Derek CookRitual Theory, Ritual Practice: Unlocking the Secrets of...
Rituals have been an...

 Evan Hayes
Evan HayesStop the Itch: Simple Steps to Lasting Relief
Itching, an...

 Herman Mitchell
Herman MitchellThe Ultimate Premarital Guide: Your Essential Wedding...
Congratulations on your engagement! This is...

 DeShawn Powell
DeShawn PowellUnlocking the Enigma of the Mantle: A Deep Dive into "The...
Our planet,...
4.4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 44788 KB |
| X-Ray for textbooks | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 276 pages |